The primary goal of an agile learning environment

Differentiated learning awareness is promoting a movement towards adjustment and adaptation of, content, process, product and the learning environment. Patrick Byrne explains ‘agile learning environments’, and how technology supports them.
An agile learning environment is an educational playground that is intentionally designed to be adjustable, exchangeable and moveable. The learning space is designed to support idea generation, collaboration and experimentation. agile learning environments ultimately showcase how the design of a physical space, as well as the implementation of technology within that space, can shift how people communicate with one another.
The primary goal of an agile learning environment is flexibility. The furniture in the space, and the technology used within it, are flexible so that it can be configured and re-configured to suit different approaches to learning and teaching. An agile learning environment has the ability to turn a static or ‘dead’ space into a dynamic space. It can also include the re-purposing and use of non-traditional spaces such as hallways and communal zones as impromptu learning spaces.
The open-air Maekong Markets outside Bangkok are a great example to show how a space can be transformed from one purpose to another in the matter of seconds. The markets lie on an active train track. Vendor tents flank the route and wares lie inches from the track. Whenever a train approaches, the awnings and shop fronts are moved back from the rails. Once the train passes, shopping resumes almost immediately. This happens about eight times a day. Although it is a consumer space rather than a learning space, The Maekong Markets are a good example of how flexible learning spaces might work.
Like the railway markets, agile classrooms are ones that can be easily altered and rearranged to provide a diversity of didactic opportunities. The furniture should be flexible, mobile and easy to reconfigure so that both students and teachers can carry out the adaptations and new configurations by themselves within the space of minutes. The chairs and tables should also fit the size of the pupils; and ideally be easily height adjustable.
The learning environment must be highly flexible not only in terms of spatial configuration but also in relation to structure. Rather than disciplines being taught within designated time slots, in a fixed sequence, the school day flows through changing phases in which the learning space transforms to reflect each new subject and approach.
Students may alternate learning in large or small groups, project and team work, practice and repetition. Flexibility means having a choice of learning area possibilities, depending on the learning scenario, or converting a space to the appropriate learning environment without too much effort; preferably the space should be capable of ad hoc configuration.
Technology plays a vital role in an agile learning environment as it offers a range of new teaching and learning possibilities. The premise that technology improves the quality of teaching and learning has been demonstrated where technology has supported active learning, in a way which was not possible in the traditional lecture-style classroom. It’s therefore important that technology is not used to replicate the traditional schooling practices of old, but rather harnessed as part of a modern pedagogy to provide new learning experiences. Essentially, we should use the new tools to do different things, not just to do old things differently.
Below are some examples of how technology can be used to create, complement and enhance an Agile Learning Environment.
- Instead on installing a flat panel or interactive display on a wall in the classroom, it can be mounted on a trolley. This mobility enables a more dynamic use of the technology – allowing the device to transition between teacher-led sessions and student collaboration with ease.
- Wireless display solutions eliminate the need for cables, allow greater freedom of movement within the learning space and increase the ease at which one can share content from their device.
- Video conferencing expands learning beyond the confines of the classroom walls. Not only does this provide a learning platform for those in rural and remote communities, but it can also allow connections with experts and other classrooms across the world.
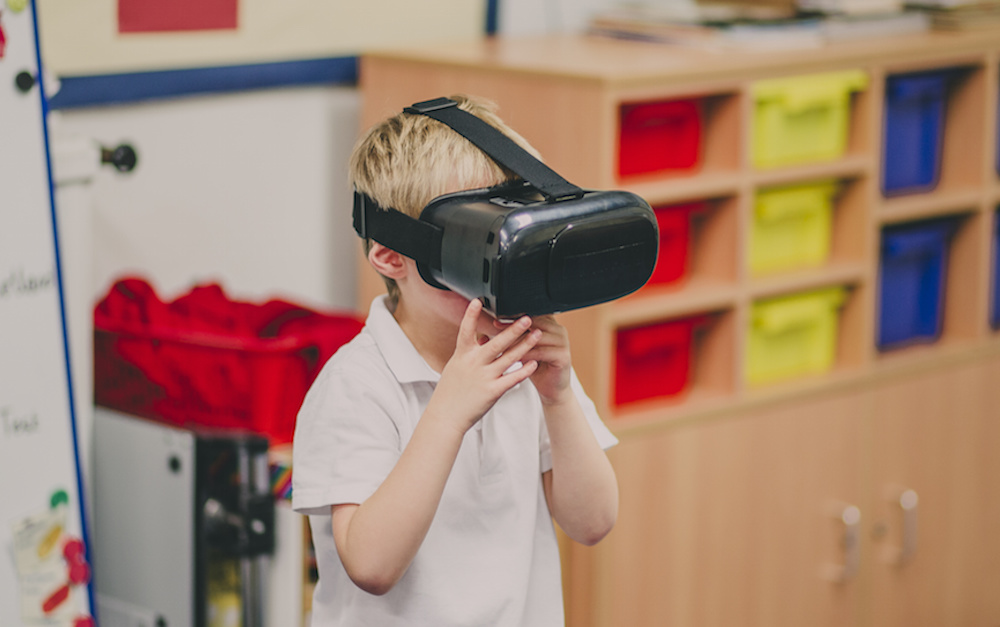
- Virtual reality enables truly immersive learning experiences. Whether it’s a virtual field trip, space exploration, navigating the human body or travelling back through time – there’s no limit to potential of virtual environments.
- The ever increasing combination of power and mobility in computers and smart devices make them invaluable within an agile learning environment. Whether it’s researching collaborating or creating have embedded themselves as an integral part of learning.
Although furniture, spatial design and technology can contribute to an agile learning environment, it’s important to emphasise that one of the most import elements of any learning environment is the teacher. Agile Learning Environments are not a substitute for quality teaching, but rather a way of supporting it.
Teachers have an important, and evolving, role in teaching in agile environments. The take-up of the opportunities provided by technology in these spaces relies on teachers identifying and using this potential.
Ongoing training and support is also essential to maximising the use of any technology used in an agile learning environment. As educational futurist, David Thornburg says, “if you bring in these technologies and don’t think ahead to how they’ll be used to promote learning and the acquisition of skills, then the only thing that will change in the school is the electric bill”.